| Case Name |
A fire occurred during making decorations for a parade car |
| Pictograph |
|
| Date |
February 5, 1995 |
| Place |
Ono, Hyogo, Japan |
| Location |
A factory |
| Overview |
On making parade decorations, an acetone fire occurred due to mishandling of acetone used as a solvent. The cause was a lack of safety education in small amount of dangerous material (acetone) used at the factory. |
| Incident |
Careless handling of dangerous materials (acetone) at a factory where a small amount of dangerous material was used, and a fire occurred. |
| Processing |
Consumption and Usage |
| Substance |
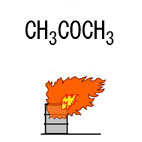
Acetone, Fig2 |
| Type of Accident |
Fire |
| Sequence |
Decorations for a parade car were being made using foam polystyrene. The foam polystyrene was cut with a hot nichrome wire after it was dissolved using acetone. The acetone ignited, and there was a fire. |
| Cause |
The remaining used acetone was ignited due to a high temperature of the nichrome wire. This was caused due to careless handling of dangerous materials. |
| Response |
Public fire fighters turned out. |
| Countermeasures |
As the employees did not know the danger of acetone, which is readily available and is widely used, it is important to carry out safety education of employees. |
| Knowledge Comment |
They did not recognize the danger of acetone, which is equivalent to gasoline because its ignition point is -18 °C. A small amount of flammable material is sufficient to cause a fire. As it is not necessary to notify the fire department on using a small amount of dangerous material, consideration of safety was not sufficient. |
| Background |
The employees did not recognize the danger of acetone. Moreover, the problem is whether a responsible person of the factory had recognized the risks, had prepared safety facilities, or had educated the employees. |
| Incidental Discussion |
Consideration of safety might not have been sufficient, because the approval of the fire brigade and notification to it were not necessary on handling a small amount of dangerous material in general factories. |
| Reason for Adding to DB |
Example of fire caused due to insufficient understanding of dangerous substances |
| Scenario |
| Primary Scenario
|
Poor Value Perception, Poor Safety Awareness, Inadequate Risk Recognition, Ignorance, Insufficient Knowledge, Insufficient Knowledge and Experience, Malicious Act, Rule Violation, Safety Rule Violation, Planning and Design, Poor Planning, Secondary Damage, External Damage, Fire
|
|
| Sources |
Major cases of accidents in 1995 - Accidents with death or injury, and monetary damage of ¥ 10 million or more - Industry and Safety Vol.12 No.41 p.7 (1996).
|
| Number of Injuries |
5 |
| Financial Cost |
¥ 2 million (Fire and Disaster Management Agency) |
| Multimedia Files |
Fig2.Chemical formula
|
| Field |
Chemicals and Plants
|
| Author |
KOSEKI, Hirosi (National Research Institute of Fire and Disaster)
TAMURA, Masamitsu (Center for Risk Management and Safety Sciences, Yokohama National University)
|