| Case Name |
Fire of heptane due to improper valve handling at a polypropylene manufacturing plant |
| Pictograph |
|
| Date |
July 26, 1989 |
| Place |
Ichihara, Chiba, Japan |
| Location |
Chemical factory |
| Overview |
A fire occurred at the solvent scrubber in the solvent recovery process of the polypropylene manufacturing plant on July 26th, 1989. AS the local flow meter at the bottom of the solvent scrubber clogged, repair was carried out. The flow meter drain valve was opened for confirmation before repair started. Heptane flowed out from the drain valve. It was judged that the flow meter inlet valve had not closed perfectly. A large quantity of heptane flowed out, although an attempt was made to close the inlet valve with the drain valve opened. Although an attempt for closing the drain valve and opening the block valve was made, the heptane ignited, and caught fire. With the outbreak of fire, the emergency shutdown system operated, and the plant shut down. |
| Incident |
As the flow meter at the bottom of the scrubber in the solvent recovery process of the polypropylene manufacturing plant clogged, preparatory work for repair was carried out. Heptane leaked because the flow meter drain valve was opened at that time, then it ignited, and there occurred a fire. Refer to Fig2. |
| Processing |
Manufacture |
| Individual Process |
Distillation |
| Process Flow |
Fig2.Process flow chart
|
| Substance |
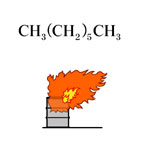
Heptane, Fig3 |
| Type of Accident |
Leakage, fire |
| Sequence |
As the local flow meter at the bottom of the solvent scrubber clogged, a repair was requested.
04:00 on July 26th, 1987. The repair preparation work was executed.
07:45. The repair work was taken over to the next shift.
08:25. The flow meter inlet valve was closed. The drain valve of the flow meter block was opened. A heptane leak was seen at the drain valve. It was judged that the flow meter inlet valve was not completely closed. A large quantity of heptane flowed out, although efforts were made to close the inlet valve while the drain valve was opened.
08:30. A fire occurred. Attempts to close the inlet valve were interrupted.
08:30. Simultaneously with the fire, the plant was shut down by the emergency shutdown system.
08:48. Disaster control headquarters was set up, and disaster-prevention activities were started.
09:00. It came in under the supervision of public fire fighting service.
09:29. Introduction of nitrogen gas into the plant was started.
10:00. It was confirmed the fire had been extinguished. |
| Cause |
1. The stopper of the handle of the inlet valve was deformed. The handle did not stop at the correct position when the handle was turned to close the valve. The outflow of heptane did not stop, and the flow rate increased.
2. The cause of the ignition of heptane that flowed out is presumed to be static electricity. |
| Response |
1. The plant shut down and emergency blow-down were conducted automatically with operating the emergency shutdown system.
2. Disaster control headquarters was set up.
3. Nitrogen gas was introduced into the plant. |
| Countermeasures |
1. Enhancement of safety education on valve operation, etc.
2. Strengthening inspection of equipment and machinery. |
| Knowledge Comment |
When a valve is opened and hazardous materials leak, the valve should be closed at once. Other work must be carried out after the leakage of hazardous materials is stopped. |
| Background |
The drain valve must be closed when the upstream flow meter inlet valve is operated. As the procedure was done incorrectly, the fire occurred. It seems that education on the basis of valve operation was insufficient. It is prohibited to carry out other work while the drain valve is opened, except for draw-off work. |
| Reason for Adding to DB |
Example of accident caused due to a lack of a fundamental knowledge on operating procedure. |
| Scenario |
| Primary Scenario
|
Organizational Problems, Inflexible Management Structure, Insufficient Education/Training, Carelessness, Insufficient Understanding, Insufficient Recognition of Risk, Usage, Maintenance/Repair, Left the Mal-Function, Regular Operation, Erroneous Operation, Procedure Discrepancy, Failure, Deformation, Leakage by Valve not Closed, Secondary Damage, External Damage, Fire, Loss to Organization, Economic Loss, Direct Monetary Damage 45 milion yen
|
|
| Sources |
Fire and Disaster Management Agency, Case of major accident, Fire occurred when heptane leaked during deliquoring operation for detaching flow meter from drain and it ignited, Accident cases of dangerous materials, pp.33,50-51(1989)
High Pressure Gas Safety Inst. of Japan, High-pressure gas protection overview, pp.222-223(1990)
High Pressure Gas Safety Inst. of Japan, Polypropylene manufacturing equipment, Fire involving butane that leaked from solvent scrubber bottom flowmeter, Accident examples of Petroleum refinery and Petrochemical units, pp.125-130(1995)
|
| Number of Injuries |
1 |
| Physical Damage |
Within a range of about 80 square m around the ignition point, electricity, insulation of piping, instruments were damaged, and paint peeled off. 390 L butane burned. |
| Financial Cost |
¥ 45 million. (Accident cases of dangerous materials) |
| Multimedia Files |
Fig3.Chemical formula
|
| Field |
Chemicals and Plants
|
| Author |
OGAWA, Terushige (Graduate School of Environment and Information Sciences, Yokohama National University)
TAMURA, Masamitsu (Center for Risk Management and Safety Sciences, Yokohama National University)
|
|